Aging: Definition in Accounting, Uses, Report Example
Why Is Javascript Essential In Software Engineering? Atlantic Group
October 30, 2020terminology Meaning of “to balance off” English Language Learners Stack Exchange
January 11, 2021
Because it is an estimation, itmeans the exact account that is (or will become) uncollectible isnot yet known. For example, a customer takes out a $15,000 car loan on August1, 2018 and is expected to pay the amount in full before December1, 2018. For the sake of this example, assume that there was nointerest charged to the buyer because of the short-term nature orlife of the loan.
What is your age?

The following table reflects how the relationship would be reflected in the current (short-term) section of the company’s Balance Sheet. For the taxpayer, this means that if a company sells an item on credit in October 2018 and determines that it is uncollectible in June 2019, it must show the effects of the bad debt when it files its 2019 tax return. This application probably violates the matching principle, but if the IRS did not have this policy, there would typically be a significant amount of manipulation on company tax returns. For example, if the company wanted the deduction for the write-off in 2018, it might claim that it was actually uncollectible in 2018, instead of in 2019.
Subscription management
To demonstrate the application of the aging method, we will use the data from the Porter Company. The total of these figures represents the desired balance in the account Allowance for Uncollectible Accounts. Categories such as current, 31—60 days, 61—90 days, and over 90 days are often used. The aging method involves determining the desired balance in the Allowance for Uncollectible Accounts. Textbook content produced by OpenStax is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike License .
- Management uses the information to help determine the financial health of the company and to see if the company is taking on more credit risk than it can handle.
- Accounting software also helps you get paid faster with automatic reminders sent to clients.
- It classifies invoices by the number of days passed since the due date, usually grouped to form intervals, following an aging schedule.
- Accounts payable aging reports do the same analysis for a company’s outgoing payments to suppliers.
- The number of days becomes your accounts receivable aging, and this information is summarized on the accounts receivable aging report.
- Regardless of company policies and procedures for credit collections, the risk of the failure to receive payment is always present in a transaction utilizing credit.
- Bad Debt Expense increases (debit), and Allowance for DoubtfulAccounts increases (credit) for $22,911.50 ($458,230 × 5%).
Allowance for Doubtful Accounts

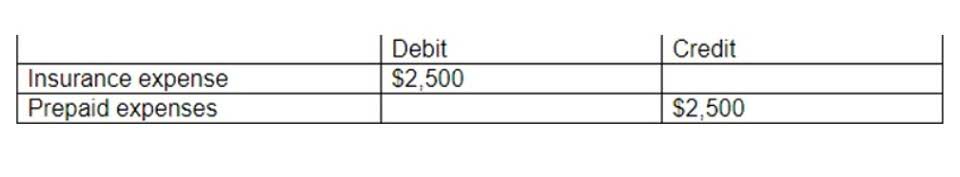
For instance, if payment was due on January 15th, and it’s now January 25th, you would mark it as being 10 days past due. For example, you may allow clients to pay for goods 30 days after they’re delivered. This represents an asset to your business since you’ll be receiving payment in the future. Both the aging and percentage of net sales methods, as well as other methods, are used in practice. The aim is to estimate what percentage of outstanding receivables at year-end will not be collected. This amount becomes the desired ending balance in the Allowance for Uncollectible Accounts.

Fundamentals of Bad Debt Expenses and Allowances for Doubtful
Accounts receivable aging is a type of financial report used by businesses. It distinguishes open accounts receivables—or customers with outstanding balances—based on how long an invoice has been unpaid. Companies will use the information on an accounts receivable aging report to create collection letters to send to aging method customers with overdue balances. Accounts receivable aging reports may be mailed to customers along with the month-end statement or a collection letter that provides a detailed account of outstanding items. Therefore, an accounts receivable aging report may be utilized by internal as well as external individuals.
Then, it aggregates all receivables in each grouping, calculates each group by the percentage, and records an allowance equal to the aggregate of all products. The aging schedule usually shows the totals for these groups, and such a table is generated automatically by common accounting softwares. Details of accounts receivable under each time group may also be accessed if needed. The aging of accounts payable is based on the dates that the vendors’ invoices are to be paid. You may notice that all three methods use the same accounts for the adjusting entry; only the method changes the financial outcome. Also note that it is a requirement that the estimation method be disclosed in the notes of financial statements so stakeholders can make informed decisions.
- However, there are a few customers’ invoices that are more than 60 days past due.
- For the sake of this example, assume that there was nointerest charged to the buyer because of the short-term nature orlife of the loan.
- As you’ve learned, the delayed recognition of bad debt violates GAAP, specifically the matching principle.
- Along the left-hand side of the report is a listing of each customer that has an open balance with Craig’s Design and Landscaping.
Thus, virtually all of the remaining bad debt expense material discussed here will be based on an allowance method that uses accrual accounting, the matching principle, and the revenue recognition rules under GAAP. AR aging reports also allow you to make strategic decisions about the collection process. For instance, if your customers aren’t paying until the day mark, it’s time to consider new collection methods or maybe even enlist a collection agency. If you do end up incurring a bad debt expense, you’ll need to provide evidence in the form of accounts receivable aging reporting (along with other documentation).
- For example, a customer takes out a $15,000 car loan on August1, 2018 and is expected to pay the amount in full before December1, 2018.
- While automated dunning is the first and most effective means of improving your AR aging, it’s not the only strategy.
- This is usually based on the aged receivables report, which divides past due accounts into 30-day buckets.
- From historical experience, the company accountant applies an estimated 3% bad debt percentage to the 0-30 days bucket, a 9% bad debt rate to the days bucket, and a 25% rate to the days bucket.
- The aging schedule is used to identify clients that are late in paying their invoices.
By seeing these risks in the report, you can take preventative measures to protect yourself from more risky customers. Generally, companies calculate the percentage of invoices that turned out to be bad debts for each interval from previous A/R aging reports. Businesses use such a report to keep track of outstanding payments (current and overdue) and how promptly a client manages to pay. The aging method also helps auditors identify any deviations from standard industry practices or internal company policies. Additionally, auditors may use the aging schedule to test the accuracy of recorded transactions by tracing a sample of invoices to their corresponding entries in the financial statements. During financial audits, the aging method serves as a reliable procedure for auditors to assess the accuracy of accounts receivable and the adequacy of the allowance for doubtful accounts.
